


Surgverse: Video World Foundation Models for Surgery
Augmented Situational Awareness and Dexterity in Robot-Assisted Surgeries through Foundation Model Post-Training
Ruixing Liang1,3,4*, Zhaoshuo Li2, Qian Luo2, Fengyi Jiang1, Xiaorui Zhang1, Lingbo Jin1, Sierra Bonilla1, Hongchao Shu4, Zhuohong He1, Chinedu Nwoye1, Adam Schmidt1, Jingpei Lu1, Abdullah Jamal1, Omid Mohareri1
1Intuitive Surgical · 2Johns Hopkins University · 3NVIDIA · 4University of Maryland
*Work done during internship at Intuitive Surgical
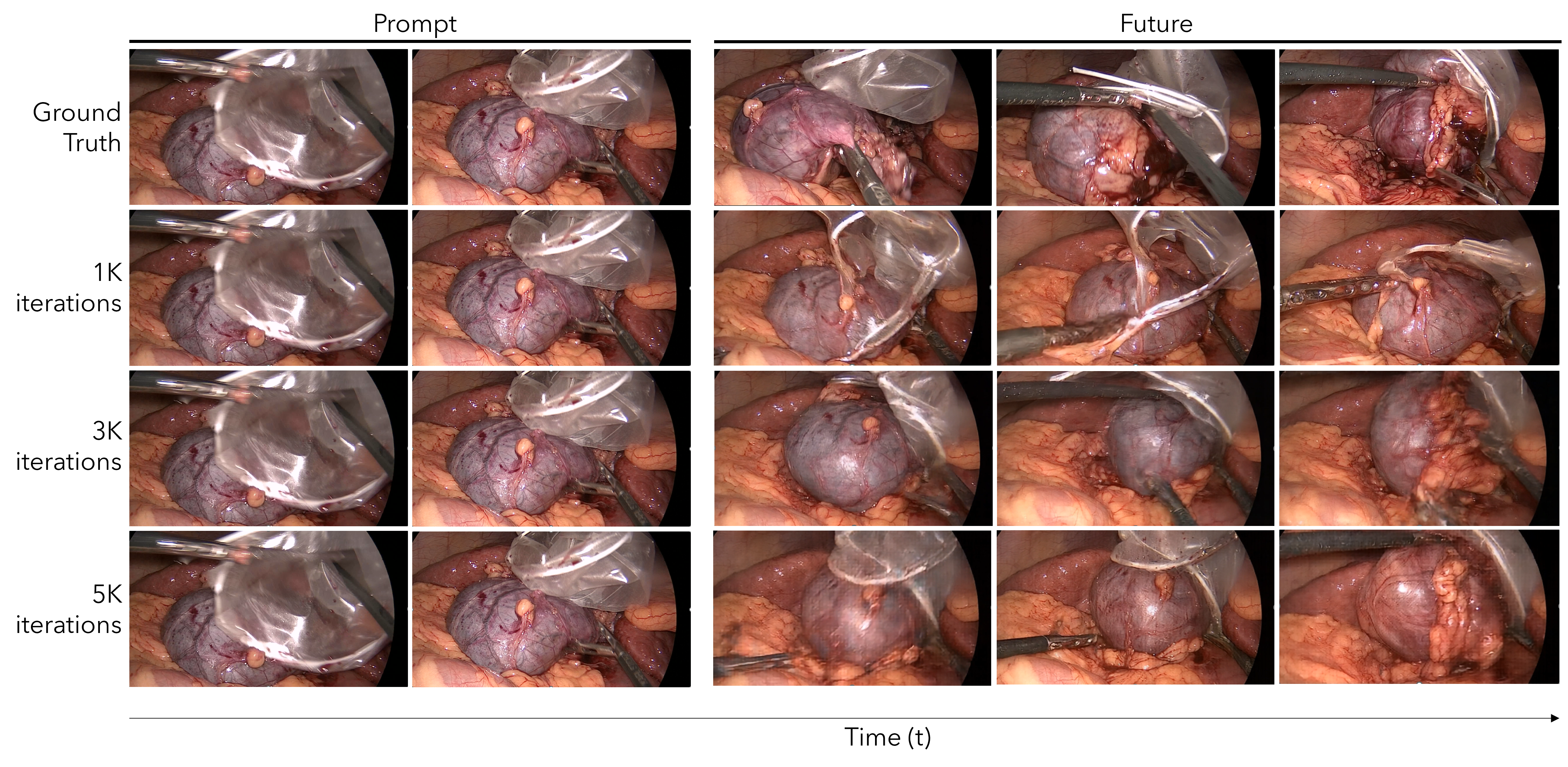
Future Prediction
Based on a current situation it could predict what's gonna happen shortly.
Ground Truth
Prediction #1
Prediction #2
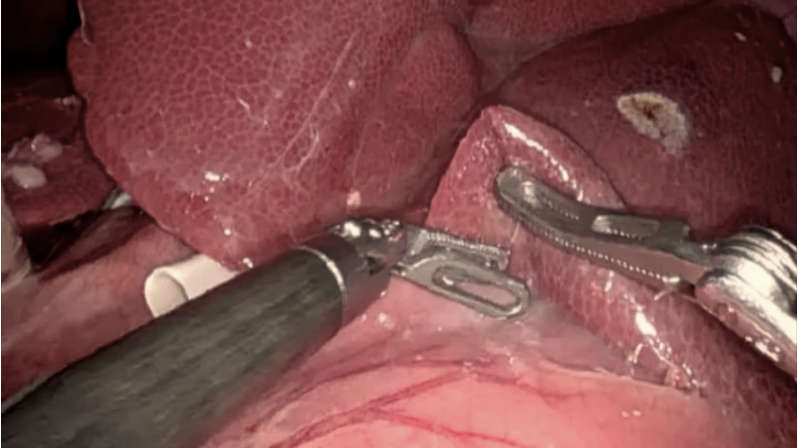
Input Frame
Ground Truth
Model Prediction
Style Transfer
Apply photorealistic texture on simulation data or augment current annotated dataset with certain variations.
Raw Video
Segmented Raw Video
Gen #1
Gen #2
Gen #3
Camera Control Comparison with SOTA
Based on a current situation it could recreate it via a new view point (Virtual Camera).
Ground Truth | Surgverse #1
Surgverse #2
CogVideo
Veo (Google)
Abstract
Video world foundation models (WFMs) offer realistic physical simulation through video generation, enabling applications like autonomous driving and robotics. However, surgical applications demand unprecedented levels of visual fidelity, geometric precision, and action controllability—requirements unmet by existing general-purpose models.
We present Surgverse, the first specialized video world foundation model for robot-assisted surgery. Through systematic post-training of high-resolution video diffusion models on multimodal surgical data, we achieve state-of-the-art performance across four novel surgical-specific metrics.
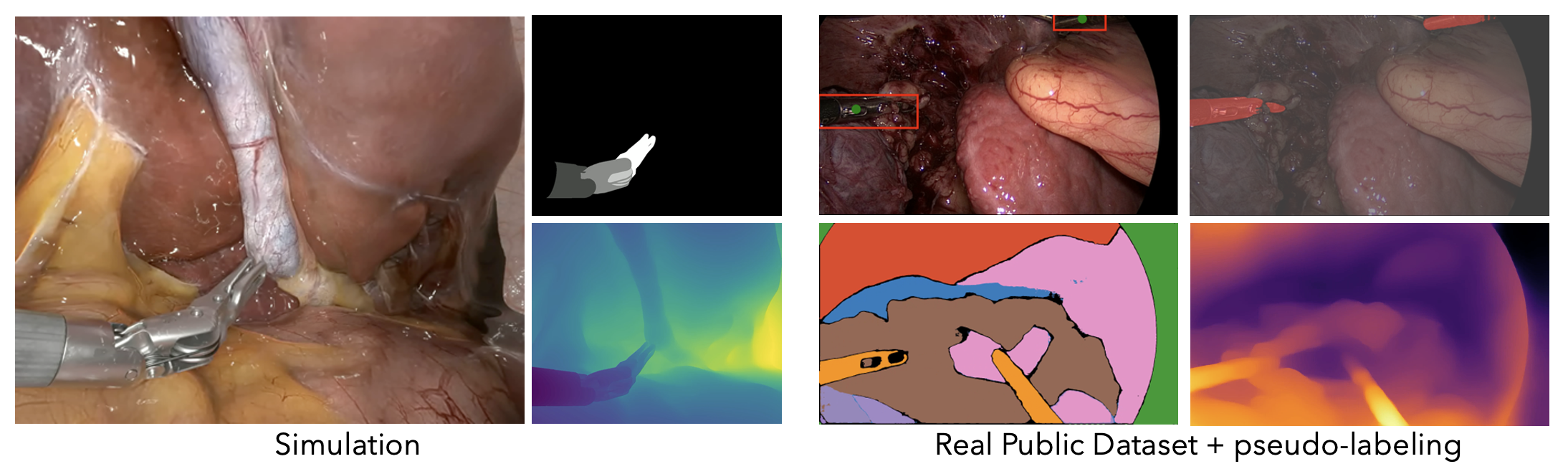
Multimodal Data Pipeline
Hybrid surgical dataset combining simulation and real-world data with semantic segmentation, depth, and action annotations.
Two-Stage Post-Training
LoRA-based domain adaptation followed by multimodal ControlNet training for precise surgical generation.
SurgBench Evaluation
Clinically-grounded benchmark with four novel metrics for surgical-specific video quality assessment.
Surgical Complexity Problem
Complex Lighting Dynamics
Specular highlights and dynamic shadows create challenging illumination conditions that previous models struggle to replicate with surgical precision.
Non-Rigid Tissue Deformations
Biological tissues undergo complex, continuous deformations that demand sophisticated physical simulation capabilities.
Instrument Occlusions
Surgical instruments frequently occlude tissue and anatomical features, requiring robust handling of partial visibility and spatial reasoning.
Clinical-Resolution Fidelity
Surgical applications demand high-resolution, anatomically precise video generation for training, planning, and decision support.
The Gap: General-purpose video models lack the surgical-specific training and specialized evaluation metrics needed for clinical-grade surgical scene understanding and generation.
Surgverse Framework
Hybrid Data Curation Pipeline
Training high-fidelity World Foundation Models requires massive datasets of video paired with rich conditioning signals. We developed a hybrid data curation pipeline that combines:
Simulation-based Generation
High-fidelity surgical assets in NVIDIA Isaac Sim provide dense annotations—semantic segmentation, depth maps, and precise instrument kinematics—perfectly aligned with video frames.
Real Surgical Video Adaptation
Large-scale corpora from public surgical datasets with pseudo-labeling via foundation models (SAM2, depth estimation) fine-tuned on endoscopic data.
Two-Stage Post-Training Strategy
Domain Adaptation via LoRA
Adapt the base diffusion transformer to capture surgical-specific details—specular reflections, tissue textures, and smoke dynamics—using Low-Rank Adaptation on attention layers, conditioned on text captions.
Multimodal Control Alignment
Train auxiliary ControlNet adapters for precise control over camera viewpoint and scene geometry. Includes Anchor-ControlNet for camera trajectories with visibility-aware output masking.
Model Architecture
Surgverse builds upon the Cosmos-Transfer1 paradigm for efficient world model adaptation:
3D-VAE Latent Space
Captures both spatial and temporal information in compressed latent representations.
Flow-Matching Diffusion
Generative model in latent space with flow-based objective for stable training.
DiT Backbone
Diffusion Transformer with resolution-aware embeddings for multi-scale generation.
Efficient Inference
Post-trained weights are much smaller than full retraining, enabling practical deployment.
SurgBench: Surgical WFM Benchmark
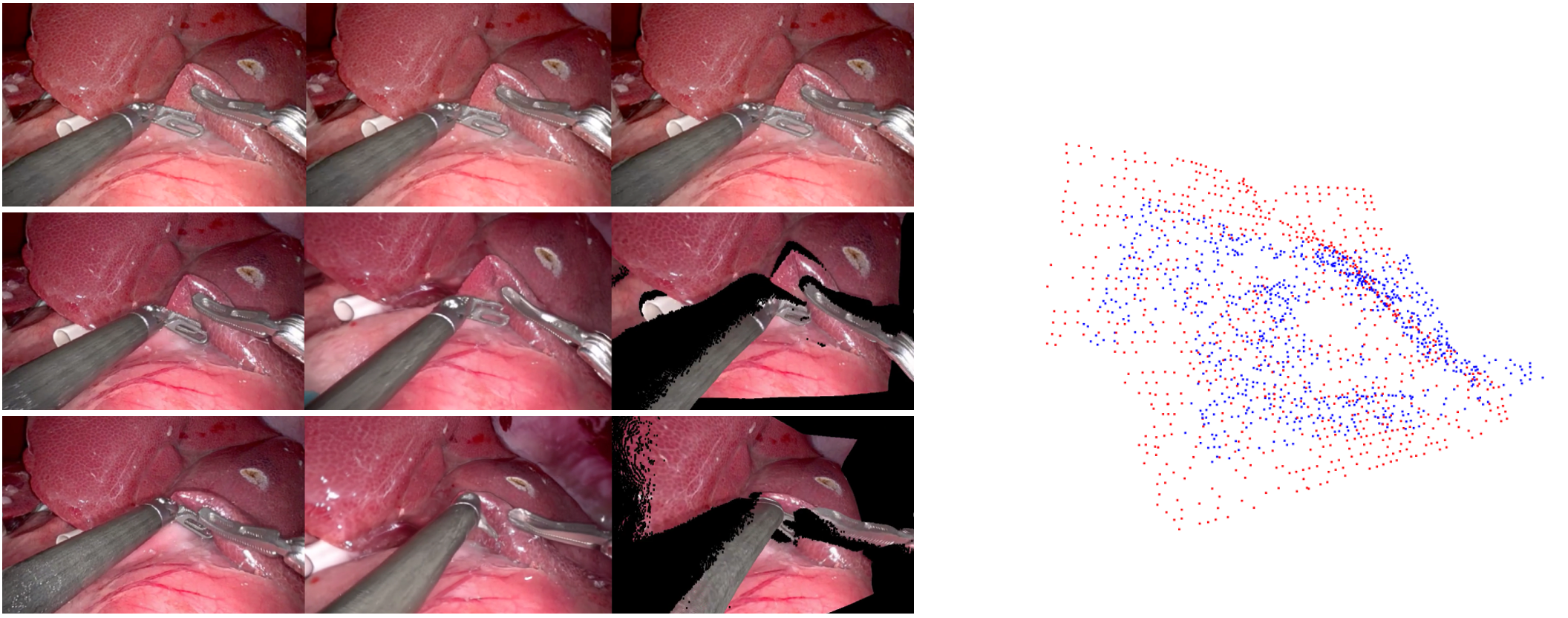
Dense point tracking for geometric coherence evaluation. Tracked points overlaid on first frame (red) and last frame (blue).
A benchmark designed to assess surgical video generation through domain-adapted metrics that capture clinical validity:
Surg-Consistency Score
Feature similarity between adjacent frames using surgical video pretrained encoders.
Geometric Coherence Score
Dense point tracking to quantify geometric drift and reprojection error under camera motion.
Pose Controllability Score
Deviation between generated camera poses and input pose commands.
Phase Recognition Accuracy
Downstream surgical phase recognition performance as a measure of clinical relevance.
Ablation Studies
Pre-Training vs Post-Training
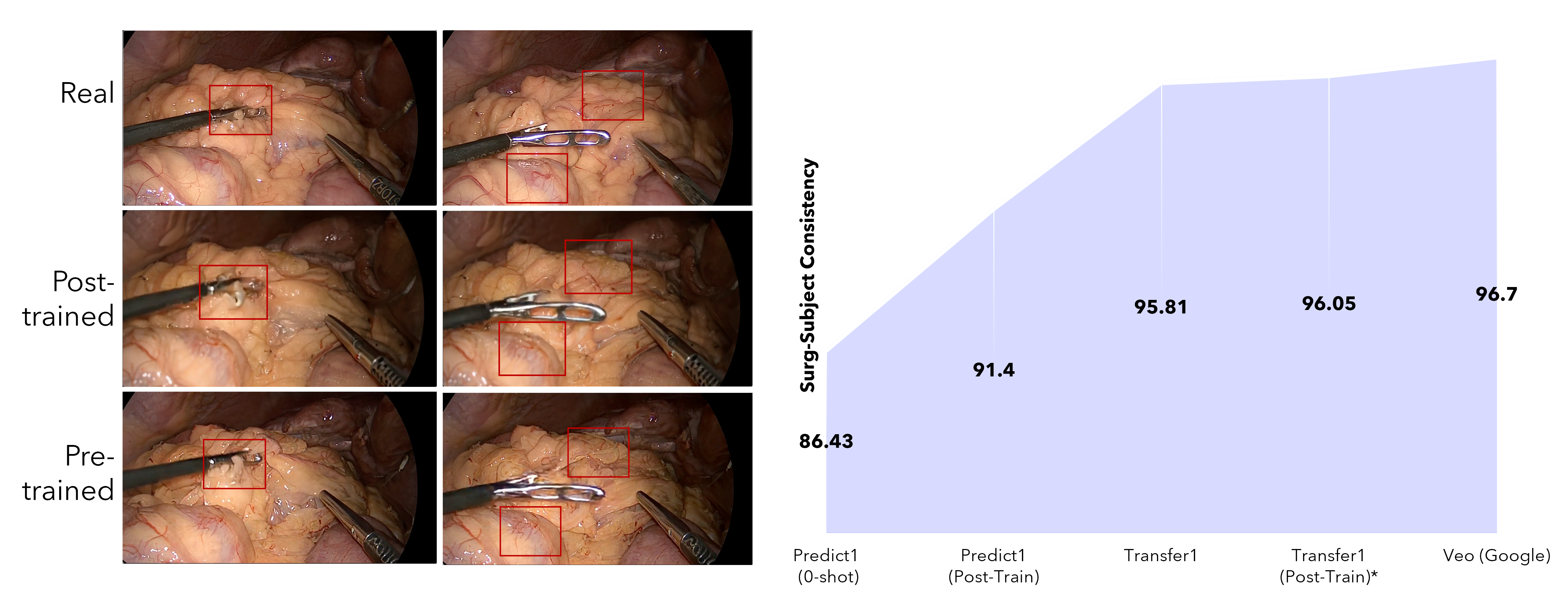
Quantitatively, the Surg-Consistency Score improves by 0.24 points for full-modality conditioned Transfer1 model and by 5.7% for Predict1 model, indicating enhanced frame-to-frame coherence and stability during long rollouts. This multimodal fusion in Transfer1 yields more stable, geometrically coherent world simulations than single-modality conditioning, demonstrating the effectiveness of structured control signals in maintaining consistent 3D spatial organization during the diffusion process. These results demonstrate the efficacy of domain-specific post-training in bridging the gap between general WFMs and the specialized requirements of robot-assisted surgery.
Data Scalability Study
To assess scalability, we systematically evaluate the impact of training data size on model performance. The Surg-Consistency score increases from 86.43 (zero-shot baseline) to 90.12 (1k training frames) and further to 91.4 (10k training frames), demonstrating that the model effectively leverages additional data to enhance temporal coherence, anatomical fidelity, and realism of tool-tissue interactions.
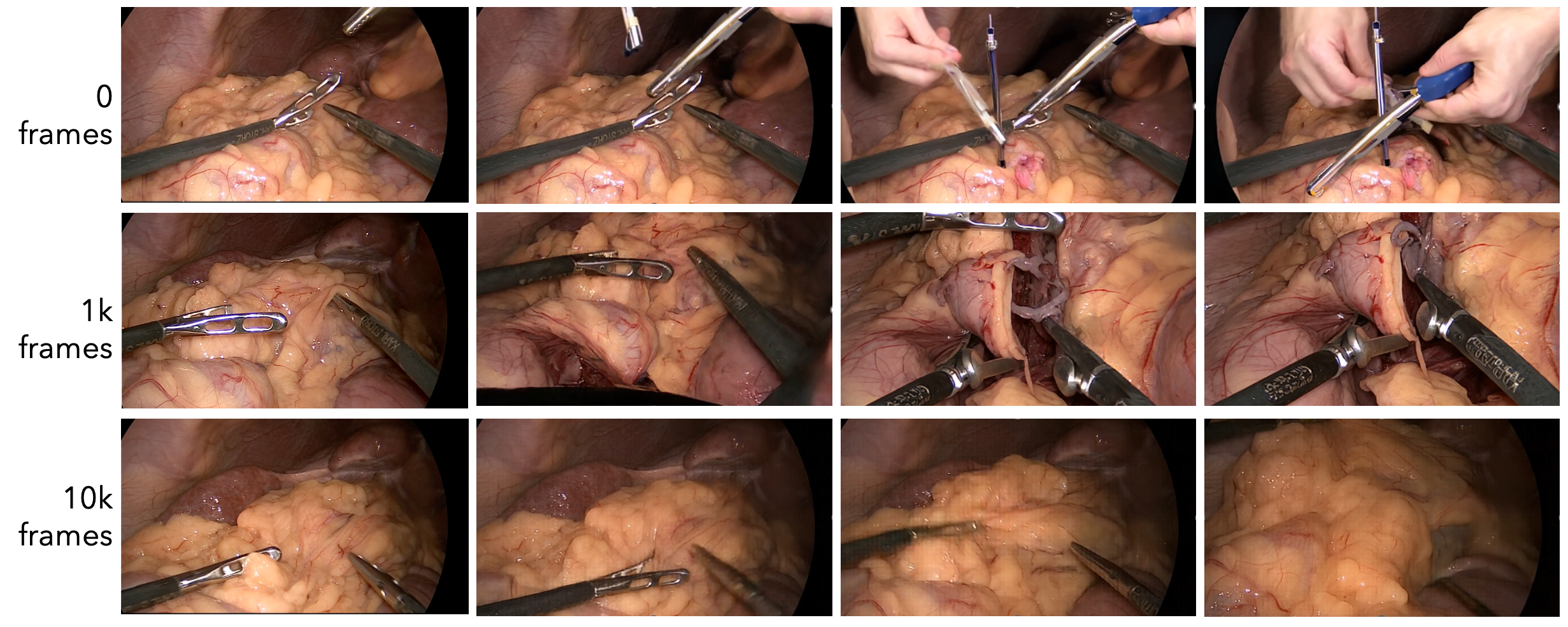
Training Iteration Study
Extended training iterations refine fine-grained details such as instrument geometry and tissue texture consistency across long rollouts. This demonstrates improvement in tool and tissue consistency (e.g., shape of the retrieval bag), and fine details of the tissue when generating long videos.
SurgBench Metrics
Novel clinically-informed evaluation framework for surgical video generation
Real-World Impact
Virtual Camera Control
Generate endoscope trajectories and surgical scene visualizations from arbitrary camera viewpoints and poses.
- →Surgeon training with dynamic viewpoint control
- →Preoperative planning with patient-specific anatomy
- →Intraoperative augmented visualization systems
Enables new forms of interactive surgical education and planning tools
Scalable Data Generation
Generate high-quality surgical video data for rare procedures, edge cases, and anatomical variations.
- →Data augmentation for surgical AI training
- →Edge case scenario generation
- →Anatomical variation synthesis
Addresses data scarcity in specialized surgical procedures and rare pathologies
Test-Time Prediction
Predict future surgical scenes and instrument positions to support intraoperative decision-making.
- →Model predictive control for robotic systems
- →Look-ahead visualization for surgeons
- →Counterfactual outcome prediction
Enhances surgical precision and safety through predictive guidance
Quantitative Comparison
| Model | Surg-Consistency ↑ | Geo-Coherence ↑ | RPE Trans (mm) ↓ | RPE Rot (deg) ↓ |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Predict1 (0-shot) | 86.43% | — | — | — |
| Predict1 (Post-Train) | 91.4% | — | — | — |
| Transfer1 | 95.81% | — | — | — |
| Transfer1 (Post-Train) | 96.05% | — | — | — |
| Veo (Google) | 96.72% | 1.5 | 1.2 | 1.8 |
| CogVideo | — | 1.9e-4 | 2.1 | 0.3 |
| Wan2.1 | — | 2.7e-4 | 3.5 | 0.1 |
| Ours (Anchor Video)⭐ BEST | — | 5.57e-4 | 0.055 | 0.06 |
Legend: Surg-Consistency measures temporal coherence using a surgical video encoder (higher is better). Geo-Coherence is geometric reprojection error (lower is better). RPE measures camera pose deviation in translation (mm) and rotation (degrees).
Citation
BibTeX
@article{liang2025surgverse,
title={Surgverse: Video World Foundation Models for Augmented Situational Awareness and Dexterity in Robot-Assisted Surgeries},
author={Liang, Ruixing and Li, Zhaoshuo and Luo, Qian and others},
journal={arXiv preprint},
year={2025}
}About This Work
This research was conducted by teams at Intuitive Surgical, NVIDIA, and Johns Hopkins University.
Submitted to CVPR 2026